Evaluation
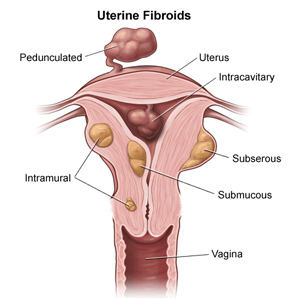
Submucosal, Intramural and Subserosal Fibroids
Submucosal fibroids
These fibroids are located just underneath the endometrium, or lining of the uterus, and protrude into the uterine cavity. Submucosal fibroids can vary in how much of the fibroid protrudes into the uterine cavity and how much is in the muscle of the uterus. They often cause heavy bleeding and long periods, but they can also cause irregular bleeding.
Intramural fibroids
These fibroids are found predominantly in the myometrium, or muscle of the uterus. Depending on their size and location, these fibroids can also extend toward and distort the uterine cavity or protrude outside the uterus. Intramural fibroids can be asymptomatic (causing no symptoms), cause bleeding abnormalities, or cause pressure and bulk symptoms, such as pelvic pain, lower back pain and urinary frequency.
Subserosal fibroids
These fibroids are located near the outside of the uterus. They can be partially in the myometrium (muscle of the uterus) or hanging off the outside of the uterus. They can cause bulk and pressure symptoms such as bladder or rectal pressure, lower back pain or pelvic pain.
Pedunculated fibroids
Pedunculated fibroids are located either inside or outside of the uterus and are attached with a thin stalk.
Intracavitary fibroids
Intracavitary fibroids are located fully inside the intrauterine cavity.

